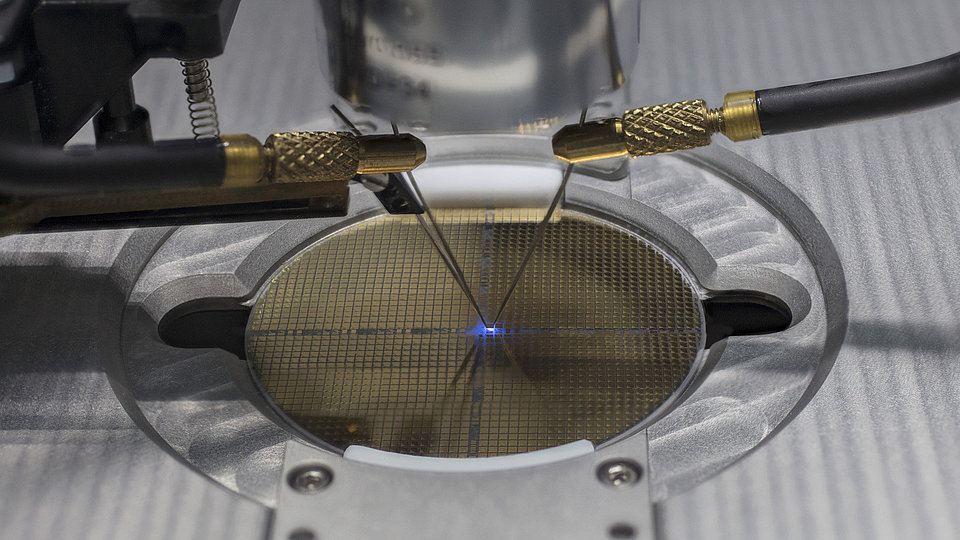
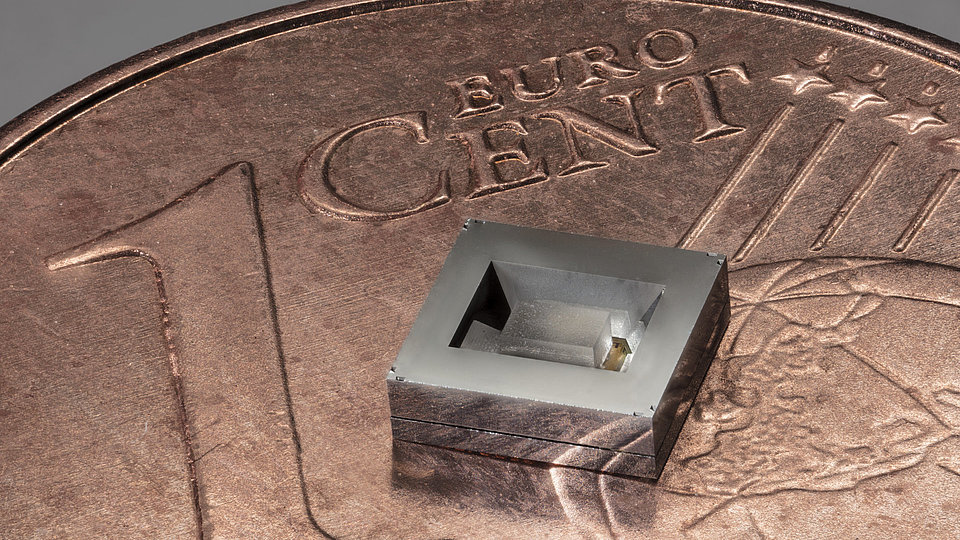
UV Light Emitting Diodes (UV-LEDs)
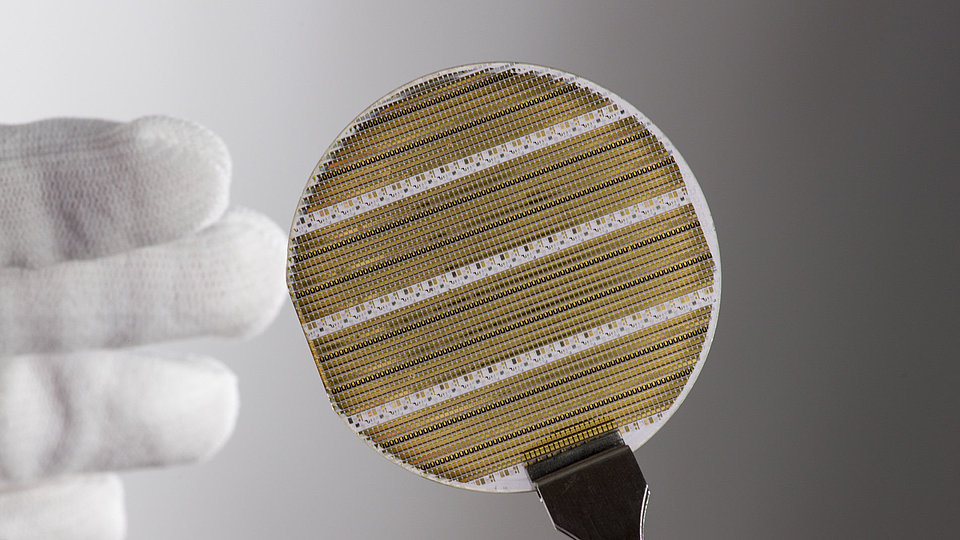
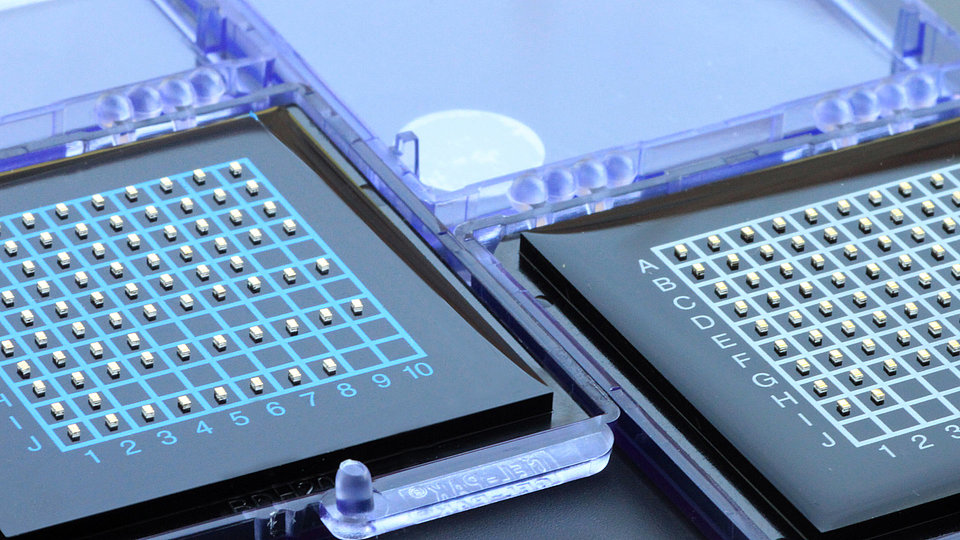
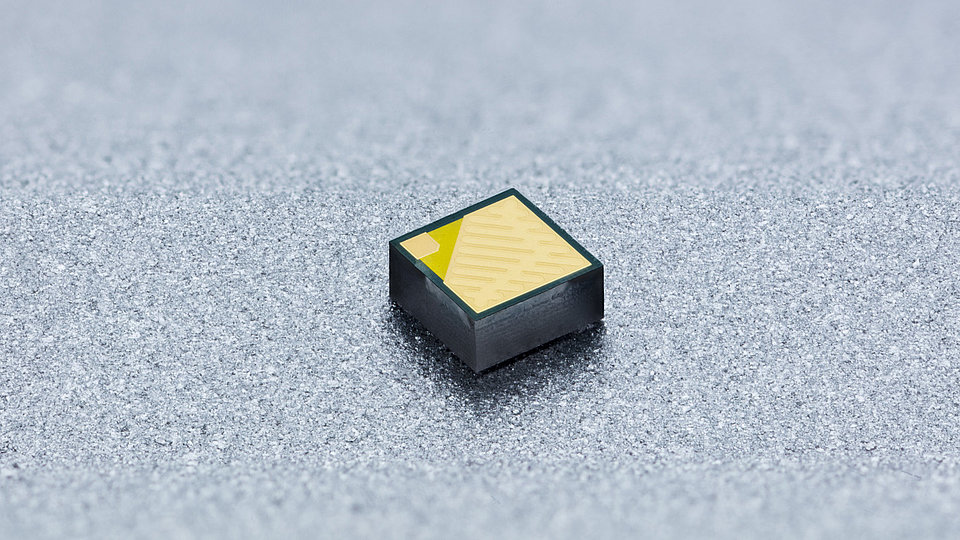
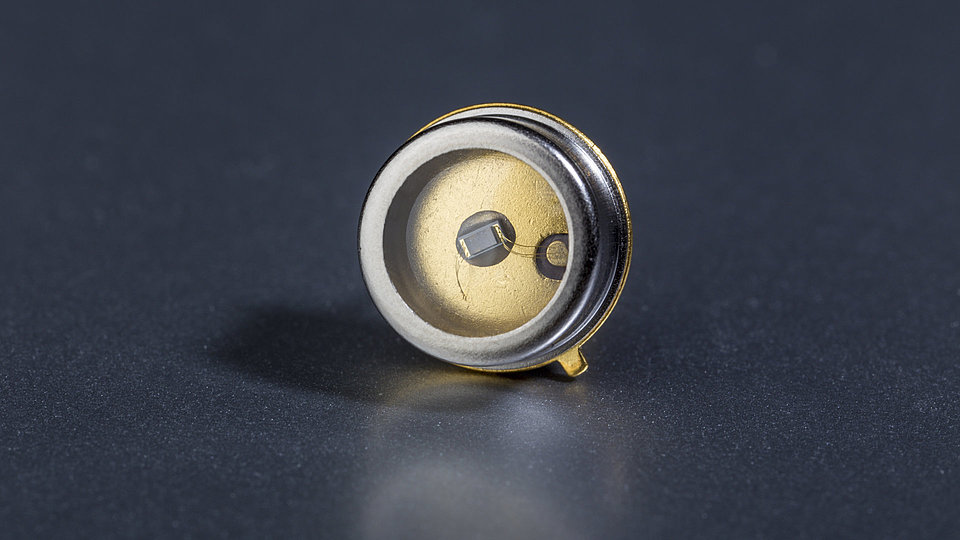
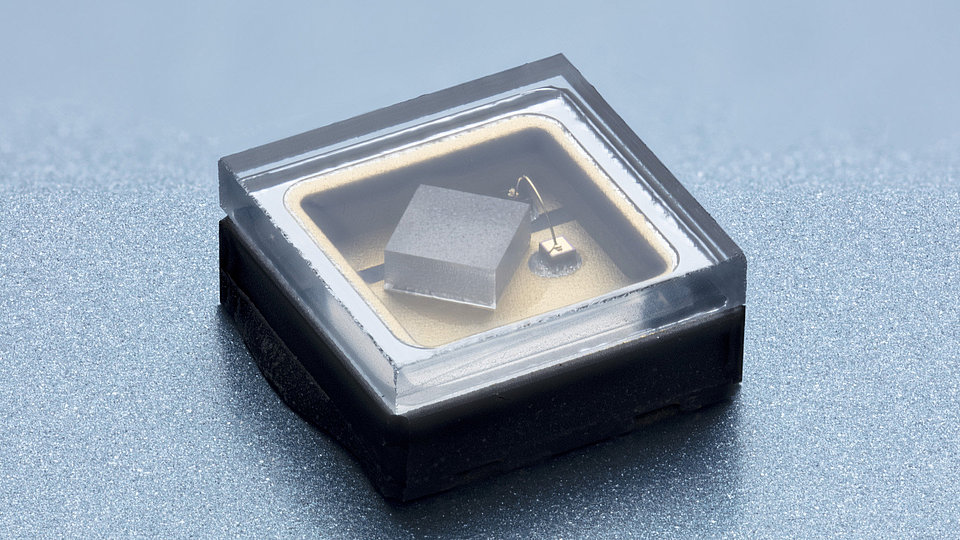
We develop (In)AlGaN-based light-emitting diodes (LEDs) with emission in the ultraviolet (UV) spectral region. The research work takes place in close cooperation with the TU Berlin within the Joint Lab GaN Optoelectronics. Activities include device simulation, design, epitaxy of (InAlGa)N heterostructures, device chip fabrication, assembly and characterization.
Advantages of our UV-LEDs at a glance
- emission wavelength can be adjusted to the respective application by adapting the heterostructure
- small, compact and robust
- can be operated at low voltages (mobile applications)
- can be switched quickly
- do not contain toxic substances
Thanks to these properties, UV LEDs are already superior to conventional UV emitters such as mercury-based gas discharge lamps in many respects. As technology advances, the advantages of UV LEDs will continue to increase.